Difference between revisions of "A20-SOM"
(→Old Linux images) |
|||
| (96 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
*RESET, RECOVERY buttons | *RESET, RECOVERY buttons | ||
*6 connectors x 40 pin 0.05" step | *6 connectors x 40 pin 0.05" step | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | == Official Images from OLIMEX == | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The recommended image for most of Olimex-made Linux boards is Olimage Linux, you can find information about it in the document here:''' | ||
| − | + | https://github.com/OLIMEX/OLINUXINO/blob/master/DOCUMENTS/OLIMAGE/Olimage-guide.pdf | |
| + | |||
| + | '''Notice this wiki article refers to outdated images and practices, if using Olimage Linux, use the information only as a reference (do not take it literally)!''' | ||
Note that only the microSD connector is suitable for booting the desired operating system, the SD-MMC connector is not suitable for booting since it is not a part of the boot sequence (refer to A20 datasheet). | Note that only the microSD connector is suitable for booting the desired operating system, the SD-MMC connector is not suitable for booting since it is not a part of the boot sequence (refer to A20 datasheet). | ||
| − | === Linux === | + | === Old Linux images === |
| − | + | ||
| + | These Debian images should be downloaded to a microSD card. You need a properly set torrent client to download the official images - they are available only as torrents. You can install the Debian to the NAND or the eMMC of your board (if it comes with one). Information on booting Debian from the NAND or eMMC might be found in these wiki article: [[how to install Debian to NAND]]; [[how to install Debian to eMMC]]. Download locations for the official images might be found below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''ALWAYS FIRST TEST WITH LATEST OFFICIAL IMAGE, NEWER HARDWARE REVISIONS OF THE BOARD MIGHT NOT WORK WITH OLDER IMAGES!!!''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| − | + | '''Latest stable official image - Debian 9 (Jessie)''' '''(recommended for all board revisions)''':''' | |
| − | + | FTP download location for the official Debian Jessie release #10 (suitable for boards with NAND): [https://ftp.olimex.com/Allwinner_Images/A20-SOM/Debian/sd/a20-SOM_mainline_uboot_GMAC_master_sunxi_kernel_3.4.103_jessie_NAND_rel_10.img.7z A20-SOM Debian Jessie with kernel 3.4.103+ for boards with NAND flash memory release 10] | |
| − | + | FTP download for A20-SOM (suitable for boards with eMMC): [https://ftp.olimex.com/Allwinner_Images/A20-OLinuXino/2.legacy_images_kernel_3.4.x/boards_with_eMMC/a20-SOM_mainline_uboot_GMAC_master_sunxi_kernel_3.4.103_jessie_eMMC_SPI_rel_13.zip A20-SOM Debian Jessie with kernel 3.4.103+ for boards with eMMC flash memory release 13] you might also want to check files and instructions in this folder on how to get boards boot from eMMC if you have troubles: [https://ftp.olimex.com/Allwinner_Images/A20-OLinuXino/2.legacy_images_kernel_3.4.x/boards_with_eMMC/sunxi-spi-emmc/ how to boot from eMMC with newer boards with 5.1 eMMC] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Image description and typical interfacing: [https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OLIMEX/OLINUXINO/master/SOFTWARE/A20/A20-build-3.4.103-release-7/USAGE-AND-COMMON-PRACTICEs-A20-Olimex_kernel_3.4.103%2B_Jessie_rel_3.txt description and basic usage of different peripherals at at the GitHub page] | ||
| − | + | Image build instructions and required files for latest Debian Jessie release might be found here: [https://github.com/OLIMEX/OLINUXINO/raw/master/SOFTWARE/A20/A20-build-3.4.103-release-7/BUILD_DESCRIPTION_A20_Olimex_kernel_3.4.103%2B_Jessie_rel_6.txt build instructions and required files at the GitHub page] | |
| − | + | You can find some older releases and older build instructions (older image revisions might be used as a reference, for testing purposes, or if you own old hardware revision of the board) at the following article: [[A20-SOM-older-releases|older releases and older build instructions]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | [https:// | + | Note: in the previous Debian releases the Ethernet was auto-detected and initialized during boot BUT this caused big delays in the start-up of the board if you didn't want to use Ethernet or if there wasn't Ethernet cable connected. |
| + | |||
| + | You can enable it by following these two steps: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. To check under what name the LAN is associated write "ifconfig –a" | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. If, for example, it is under eth0 name, then write: "dhclient eth0" | ||
| + | |||
| + | This should enable the Ethernet and then SSH would also be available. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Debian Linux file system can be extended to suit a bigger card. If the whole SD card is not used, use the following three commands to execute a script that would use all the free space of your card: | ||
| + | |||
| + | sudo su | ||
| + | resize_sd.sh /dev/mmcblk0 2 | ||
| + | reboot | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Android images === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Links to official Android releases are below. Please read description of the image carefully. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Direct download of Android 4.2.2 release 1 for NAND memory (with HDMI and 800x480 support): [https://ftp.olimex.com/Allwinner_Images/A20-SOM/Android/nand/A20_SOM_camera_LCD7_HDMI_release1.img A20-SOM Android for NAND with HDMI and 7 inch display support] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Direct download of Android 4.2.2 release 1 for microSD card (with HDMI and 800x480 support): | ||
| + | [https://ftp.olimex.com/Allwinner_Images/A20-SOM/Android/sd/A20_SOM_Android_4.22_SD_card_LCD_800x480_HDMI_release_1.img.7z A20-SOM Android for NAND with HDMI and 7 inch display support] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Build instructions and source files for the official Android images for A20 boards in this repository: https://github.com/hehopmajieh/olinuxino_configs | ||
| + | <br> | ||
== Documents == | == Documents == | ||
| Line 124: | Line 93: | ||
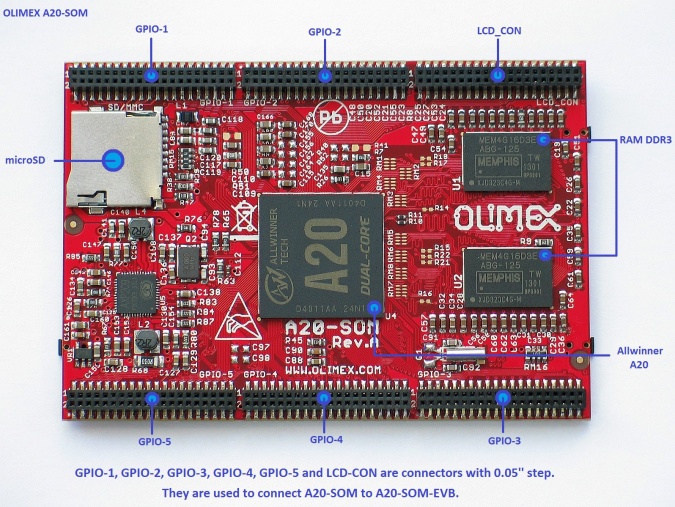
[[File:A20-SOM-1_top_named.jpg|675px]] | [[File:A20-SOM-1_top_named.jpg|675px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 138: | Line 105: | ||
===Power supply and consumption=== | ===Power supply and consumption=== | ||
| + | *'''A20-SOM'''<br><br> | ||
A20-SOM typically consumes between 0.20A and 0.25A when connected to a 5V | A20-SOM typically consumes between 0.20A and 0.25A when connected to a 5V | ||
voltage source (provided at pins GND and 5VEXT). | voltage source (provided at pins GND and 5VEXT). | ||
| Line 144: | Line 112: | ||
(tested with 'top d0'). | (tested with 'top d0'). | ||
| − | The current consumed might have peaks as high as 0.50A during start-up when | + | The current consumed might have peaks as high as 0.50A @ 5V during start-up when |
different modules are initialized. | different modules are initialized. | ||
Make sure your supply is capable of providing at least half an ampere of | Make sure your supply is capable of providing at least half an ampere of | ||
current at 5V of voltage. | current at 5V of voltage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''A20-SOM + A20-SOM-EVB'''<br><br> | ||
| + | The consumption of the combination A20-SOM + A20-SOM-EVB is betwen 0.10A and 0.15A when the A20-SOM-EVB is connected to a 12V voltage source (provided at the board's PWR jack). | ||
| + | |||
| + | During heavy load of the processor the consumption might raise up to 0.20A @ 12V | ||
| + | (tested with 'top d0'). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The current consumed might have peaks as high as 0.25A @ 12V during start-up when | ||
| + | different modules are initialized. | ||
===CAD files=== | ===CAD files=== | ||
| − | A20-SOM is considered commercial, proprietary design. The board file is not available to the customer. A pdf extracted from the original schematic is available | + | A20-SOM is considered commercial, proprietary design. The board file is not available to the customer. A pdf extracted from the original schematic is available at GitHub: [https://github.com/OLIMEX/SOM/tree/master/A20/A20-SOM A20-SOM schematics] |
| + | |||
| + | KiCAD files of the connectors of A20-SOM/A20-SOM-EVB that are perfect as a template for own design can be found here: [https://github.com/OLIMEX/SOM/tree/master/A20/A20-SOM/KiCAD%20connector%20library KiCAD templates A20-SOM] | ||
A20-SOM-EVB is considered Open Source Hardware, Eagle CAD files are available here [https://www.olimex.com/Products/SOM/A20/A20-SOM-EVB/resources/A20-SOM-EVB_eagle_sources.zip A20-SOM-EVB sources] | A20-SOM-EVB is considered Open Source Hardware, Eagle CAD files are available here [https://www.olimex.com/Products/SOM/A20/A20-SOM-EVB/resources/A20-SOM-EVB_eagle_sources.zip A20-SOM-EVB sources] | ||
The CAD product used to design OLinuXino is Eagle and you can download evaluation free version from their [http://www.cadsoftusa.com/ web site]. The evaluation version allows you to inspect the schematic and the board file sources. | The CAD product used to design OLinuXino is Eagle and you can download evaluation free version from their [http://www.cadsoftusa.com/ web site]. The evaluation version allows you to inspect the schematic and the board file sources. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== How To? == | == How To? == | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Is it possible to boot Debian from NAND? Do you provide such image?=== | ||
| + | Yes, it is possible. Use the latest Debian Jessie image and write "nandinstall". More information can be found in this wiki article: [[How_to_install_Debian_to_NAND| installing Debian Jessie to the 4GB NAND memory]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are other people who are also successful in booting Debian from the NAND. Make sure to check on the forum. Make sure to check the number of very good and optimized A20-OLinuXino Debian images by Igor Pečovnik. There are also his instructions for NAND installation of Debian: [http://www.armbian.com/download/ link to his web-site] | ||
| + | |||
===How to correctly power off OLinuXino running from NAND Flash=== | ===How to correctly power off OLinuXino running from NAND Flash=== | ||
[http://olimex.wordpress.com/2014/01/24/how-to-correctly-power-off-olinuxino-running-android/ In this Blog post] we explain what are the problems. This is common problem for all computers running OS. [http://www.linux-mtd.infradead.org/doc/ubifs.html#L_ubifs_mlc Here] you can read more about MLC NAND Flash and Linux file system. | [http://olimex.wordpress.com/2014/01/24/how-to-correctly-power-off-olinuxino-running-android/ In this Blog post] we explain what are the problems. This is common problem for all computers running OS. [http://www.linux-mtd.infradead.org/doc/ubifs.html#L_ubifs_mlc Here] you can read more about MLC NAND Flash and Linux file system. | ||
| − | ===How to | + | ===How to build the official Debian Linux image for A20-SOM? === |
| − | [ | + | Build instructions and required files for the latest Debian Jessie images: [https://github.com/OLIMEX/OLINUXINO/tree/master/SOFTWARE/A20/A20-build-3.4.103-release-2 build instructions and required files at the GitHub page] |
| − | [https://github.com/ | + | Build instructions and required files for the latest Debian Wheezy images: [https://github.com/OLIMEX/OLINUXINO/tree/master/SOFTWARE/A20/A20-build-3.4.90 instructions and files at the GitHub page] |
| − | ===How to download new Android image to the NAND memory of my A20 board?=== | + | ===How to download new Android image to the NAND memory of my A20-SOM-4GB board?=== |
| + | In order to download the Android image to the NAND memory of the board follow these steps: | ||
| − | + | 1. Install and run PhoenixSuit (can be found here: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BwplT87k9SCgaTFTZnVST05ONzA/view?usp=sharing google drive location]). | |
| − | + | 2. Download and extract the latest official image - can be found above in the Android section of this article. Make sure that the download link you visit clearly indicates that the image is suitable for the NAND memory since there are images suitable for microSD card also. The images suitable for the microSD memory and those suitable for microSD card are different. However, the upload method is almost identical – using PhoenixSuit. | |
| − | + | 3. Go to firmware tab of the program and point to the already downloaded and extracted Android image. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | 4. Disconnect the power supply and USB cable from the A20 board. | |
| − | + | 5. Press and hold RECOVERY button, apply power supply (the requirement various depending on whether you use the board stand-alone or on top of A20-SOM-EVB), release RECOVERY button. | |
| − | + | 6. Connect USB cable to the mini USB connector. | |
| − | + | 7. You will be asked for drivers for the bootloader. Navigate to the folder where you extracted the PhoenixSuit and install the drivers from the respective executable (or manually point the installer to the drivers folder in the PhoenixSuit installation path). | |
| − | + | 8. PhoenixSuit will detect the board and would ask whether you wish to also of writing the image. Choose method of writing the image and confirm your wish to write the image. | |
| + | 9. Wait till upgrade succeeds | ||
Note that it is not recommended to have your mini USB connected to an external USB hub. This might cause delays and might distort the signal levels. Always test with the USB connected straight to the USB ports of your computer. | Note that it is not recommended to have your mini USB connected to an external USB hub. This might cause delays and might distort the signal levels. Always test with the USB connected straight to the USB ports of your computer. | ||
===How do I write the official Android image to a micro SD card for my A20 board?=== | ===How do I write the official Android image to a micro SD card for my A20 board?=== | ||
| − | + | A: First download one of the official Android images, which might be found in the Android section above. | |
| + | |||
| + | Make sure that the download link you visit clearly indicates that the image is suitable for the microSD card since there are images suitable for NAND memory also. The images suitable for the microSD memory and those suitable for NAND card are different. However, the upload method is almost identical – using PhoenixSuit. | ||
| − | + | There are two types of Android images for microSD card that we usually provide and each of them has to be downloaded to a microSD card using a different method. The image provided for microSD card is either the native Android image that can be downloaded to the card via a software tool like PhoenixSuit (through the board) or an image taken from an already prepared microSD card that requires to simply write the image (through a microSD card reader). | |
| − | + | '''It is more likely that you have an Android image that requires a simple copy to a card. If that is the case you can follow the exact steps as for Linux (e.g. using "Win32 Disk Imager" or "dd" command).''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In order to prepare a microSD card with a native Android you will need a software tool called PhoenixSuit and then: | |
| − | |||
| − | + | 1. Install and run PhoenixSuit (can be found here: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BwplT87k9SCgaTFTZnVST05ONzA/view?usp=sharing download from google drive]) | |
| − | + | 2. Go to the firmware tab of the program and point to a valid Android image (note that the images on Google drive are compressed and you have to extract the archives to .img files to be able write them with PhoenixSuit) | |
| − | + | 3. Disconnect the power supply and USB cable from the A20 board. Put an SD card in micro SD holder. We recommend 4GB class 10 card. | |
| − | + | 4. Press and hold RECOVERY button, apply power supply (the requirement various depending on whether you use the board stand-alone or on top of A20-SOM-EVB), release RECOVERY button. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | 5. Connect USB cable to the mini USB connector. | |
| + | |||
| + | 6. You will be asked for drivers for the boot-loader. Navigate to the folder where you extracted the PhoenixSuit and install the drivers from the respective executables (or manually point the installer to the drivers folder in the PhoenixSuit installation path). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7. PhoenixSuit will detect the board and would ask for the method of writing the image. Choose method of writing the image and confirm your wish to write the image. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 8. Wait till upgrade succeeds | ||
Note that it is not recommended to have your mini USB connected to an external USB hub. This | Note that it is not recommended to have your mini USB connected to an external USB hub. This | ||
| Line 246: | Line 233: | ||
where X is the uSD card. | where X is the uSD card. | ||
| − | === | + | ===I don't have neither serial cable, nor HDMI monitor. I also can't access the local Ethernet network. Can I somehow access the board anyway?=== |
| + | The latest official Debian Linux image allows the use the USB_OTG connector for SSH connection without the need of a LAN cable or a serial cable. You can use a mini USB cable connected between your host PC and the on-board mini USB connector. For connection convenience there is a DHCP server running specifically for USB0 interface. The DHCP server should give IP address to the new USB0 interface of your host PC so you can make SSH connection from your PC to the default board IP address of the USB0 interface – 192.168.2.1. | ||
| − | + | You can connect to the board using a mini USB cable and an SSH client (if you use Windows you might use "puTTY", for example) at address 192.168.2.1. | |
| − | + | For Windows operating system - upon connection, the board should show up in "Windows Device Manager" as "RNDIS Ethernet Gadget". You might be asked to install a driver. The drivers can be found online as "RNDIS driver" (Remote Network Driver Interface Specification). The drivers are provided by Microsoft and they should be available for every Windows distribution - refer to the respective files and articles provided by Microsoft on how to install the required drivers. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===How to change HDMI, VGA and LCD resolutions in the official Debian image?=== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | and press "Enter". | + | The default SD card setup is made with settings for HDMI 720p/60Hz. If you want to change to some other LCD, VGA or HDMI resolution then you have to start change_display.sh script file in /root directory. When you are logged as super user in the board type: |
| + | |||
| + | For Debian Wheezy releases: ./change_display* (* = press 'tab' to auto-complete) | ||
| + | For Debian Jessie releases: change_display* (* = press 'tab' to auto-complete) | ||
| + | |||
| + | and press "Enter". | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Note that the script should be executed as super user. Under the command line interface you are automatically logged as super user (user "root", password "olimex"). However, under the graphical environment you are not auto-logged as super user and you must type "sudo" before the command (in the GUI the super-user is "olimex" and the password is "olimex")''' | ||
Then choose the resolution and the interface(LCD, HDMI or VGA). Note that the selection of a specific resolution is done by navigating with the arrow keys and pressing "space" button. Make sure the asterisk marks your selection properly. | Then choose the resolution and the interface(LCD, HDMI or VGA). Note that the selection of a specific resolution is done by navigating with the arrow keys and pressing "space" button. Make sure the asterisk marks your selection properly. | ||
| Line 267: | Line 262: | ||
*3. 10" (1024x600) | *3. 10" (1024x600) | ||
*4. 15.6" (1366x768) | *4. 15.6" (1366x768) | ||
| + | |||
Important: initially the boards are calibrated for a specific display. If you re-write the image (no matter whether the SD card or the NAND memory) you would need to use a mouse to calibrate the display initially. It might be impossible to calibrate it via touching the display. | Important: initially the boards are calibrated for a specific display. If you re-write the image (no matter whether the SD card or the NAND memory) you would need to use a mouse to calibrate the display initially. It might be impossible to calibrate it via touching the display. | ||
| Line 286: | Line 282: | ||
*14. ntsc | *14. ntsc | ||
| − | '''For VGA:''' | + | |
| + | '''For VGA:''' | ||
*0. 1680x1050 | *0. 1680x1050 | ||
| Line 298: | Line 295: | ||
*8. 1280x720 | *8. 1280x720 | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===How to edit board configurations and definitions in the official Debian Linux? === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Do you want a custom video resolution output? Do you need a different port definition? Do you need to change the hardware defitions of the board? | ||
| + | |||
| + | You would need to edit the board's script.bin/script.fex file. How to do it is described in a separate article: [[How_to_edit_board_configurations_and_definitions_in_the_official_Debian_Linux]]. | ||
===How to generate Arch Linux image?=== | ===How to generate Arch Linux image?=== | ||
| − | [http://alarma20.wordpress.com/2013/09/13/howto-build-arch-linux-arm-for-a20-olinuxino-micro/ | + | Recent forum post by user progmetalbg here: [https://www.olimex.com/forum/index.php?topic=4261.0| at Olimex forums] |
| + | |||
| + | [http://alarma20.wordpress.com/2013/09/13/howto-build-arch-linux-arm-for-a20-olinuxino-micro/ Older step by step instructions on how to build Arch Linux image for another A20 board] | ||
===How to detect and enable the Ethernet controller (if it is disabled by default)? === | ===How to detect and enable the Ethernet controller (if it is disabled by default)? === | ||
| Line 331: | Line 336: | ||
First you need to Download the [http://dl.linux-sunxi.org/users/tsvetan/ANDROID-4.2.2-SDK2.0-KERNEL-3.4/ A20 SDK2.0 Linux Kernel 3.4] | First you need to Download the [http://dl.linux-sunxi.org/users/tsvetan/ANDROID-4.2.2-SDK2.0-KERNEL-3.4/ A20 SDK2.0 Linux Kernel 3.4] | ||
| − | |||
Second you need to configure your environment read the instructions [http://source.android.com/source/initializing.html here] | Second you need to configure your environment read the instructions [http://source.android.com/source/initializing.html here] | ||
| Line 353: | Line 357: | ||
Dave from Axon instruments wrote more detailed [http://axonjakarta.wordpress.com/2014/02/14/olimex-a20-android-building-4/ blog post] about how he generates the Android image] | Dave from Axon instruments wrote more detailed [http://axonjakarta.wordpress.com/2014/02/14/olimex-a20-android-building-4/ blog post] about how he generates the Android image] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 21:39, 31 August 2023
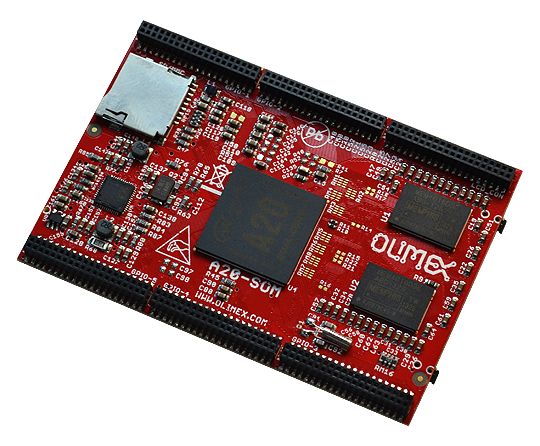
Features:
- A20 dual core Cortex-A7 processor
- 1GB DDR3 memory
- AXP209 PMU IC
- MicroSD card
- UART console
- 4GB NAND Flash
- Status LEDs
- RESET, RECOVERY buttons
- 6 connectors x 40 pin 0.05" step
Contents
- 1 Official Images from OLIMEX
- 2 Documents
- 3 Hardware
- 4 How To?
- 4.1 Is it possible to boot Debian from NAND? Do you provide such image?
- 4.2 How to correctly power off OLinuXino running from NAND Flash
- 4.3 How to build the official Debian Linux image for A20-SOM?
- 4.4 How to download new Android image to the NAND memory of my A20-SOM-4GB board?
- 4.5 How do I write the official Android image to a micro SD card for my A20 board?
- 4.6 How do I write the Linux image to a micro SD card to use with my A20 board?
- 4.7 I don't have neither serial cable, nor HDMI monitor. I also can't access the local Ethernet network. Can I somehow access the board anyway?
- 4.8 How to change HDMI, VGA and LCD resolutions in the official Debian image?
- 4.9 How to edit board configurations and definitions in the official Debian Linux?
- 4.10 How to generate Arch Linux image?
- 4.11 How to detect and enable the Ethernet controller (if it is disabled by default)?
- 4.12 How to install Android on SD-card?
- 4.13 How to access UART, I2C, GPIOs under Android?
- 4.14 How to control PWM under Linux?
- 4.15 How to build the Android 4.2.2 image for A20-OLinuXino-MICRO?
Official Images from OLIMEX
The recommended image for most of Olimex-made Linux boards is Olimage Linux, you can find information about it in the document here:
https://github.com/OLIMEX/OLINUXINO/blob/master/DOCUMENTS/OLIMAGE/Olimage-guide.pdf
Notice this wiki article refers to outdated images and practices, if using Olimage Linux, use the information only as a reference (do not take it literally)!
Note that only the microSD connector is suitable for booting the desired operating system, the SD-MMC connector is not suitable for booting since it is not a part of the boot sequence (refer to A20 datasheet).
Old Linux images
These Debian images should be downloaded to a microSD card. You need a properly set torrent client to download the official images - they are available only as torrents. You can install the Debian to the NAND or the eMMC of your board (if it comes with one). Information on booting Debian from the NAND or eMMC might be found in these wiki article: how to install Debian to NAND; how to install Debian to eMMC. Download locations for the official images might be found below:
ALWAYS FIRST TEST WITH LATEST OFFICIAL IMAGE, NEWER HARDWARE REVISIONS OF THE BOARD MIGHT NOT WORK WITH OLDER IMAGES!!!
Latest stable official image - Debian 9 (Jessie) (recommended for all board revisions):
FTP download location for the official Debian Jessie release #10 (suitable for boards with NAND): A20-SOM Debian Jessie with kernel 3.4.103+ for boards with NAND flash memory release 10
FTP download for A20-SOM (suitable for boards with eMMC): A20-SOM Debian Jessie with kernel 3.4.103+ for boards with eMMC flash memory release 13 you might also want to check files and instructions in this folder on how to get boards boot from eMMC if you have troubles: how to boot from eMMC with newer boards with 5.1 eMMC
Image description and typical interfacing: description and basic usage of different peripherals at at the GitHub page
Image build instructions and required files for latest Debian Jessie release might be found here: build instructions and required files at the GitHub page
You can find some older releases and older build instructions (older image revisions might be used as a reference, for testing purposes, or if you own old hardware revision of the board) at the following article: older releases and older build instructions
Note: in the previous Debian releases the Ethernet was auto-detected and initialized during boot BUT this caused big delays in the start-up of the board if you didn't want to use Ethernet or if there wasn't Ethernet cable connected.
You can enable it by following these two steps:
1. To check under what name the LAN is associated write "ifconfig –a"
2. If, for example, it is under eth0 name, then write: "dhclient eth0"
This should enable the Ethernet and then SSH would also be available.
The Debian Linux file system can be extended to suit a bigger card. If the whole SD card is not used, use the following three commands to execute a script that would use all the free space of your card:
sudo su resize_sd.sh /dev/mmcblk0 2 reboot
Android images
Links to official Android releases are below. Please read description of the image carefully.
Direct download of Android 4.2.2 release 1 for NAND memory (with HDMI and 800x480 support): A20-SOM Android for NAND with HDMI and 7 inch display support
Direct download of Android 4.2.2 release 1 for microSD card (with HDMI and 800x480 support): A20-SOM Android for NAND with HDMI and 7 inch display support
Build instructions and source files for the official Android images for A20 boards in this repository: https://github.com/hehopmajieh/olinuxino_configs
Documents
A20 Brief
A20 Datasheet
A20 User Manual
Hardware
Board Layout
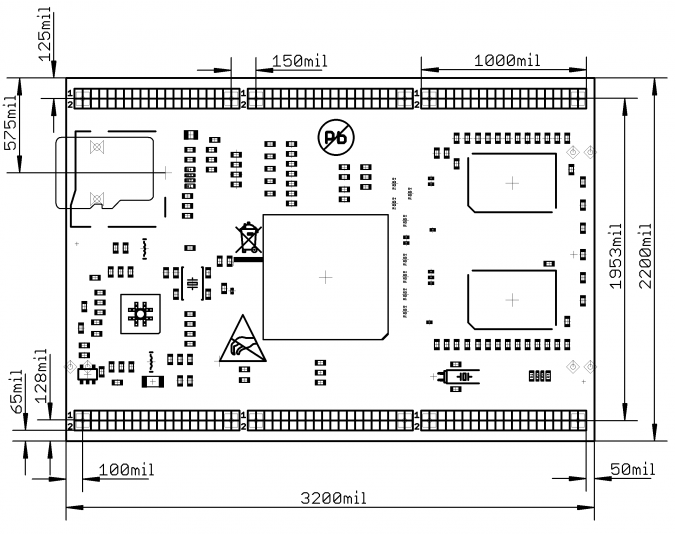
Board dimensions
A20-SOM and A20-SOM-4GB basic dimensions in mils: click
A20-SOM-EVB basic dimension in mils: click
Power supply and consumption
- A20-SOM
A20-SOM typically consumes between 0.20A and 0.25A when connected to a 5V voltage source (provided at pins GND and 5VEXT).
During heavy load of the processor the consumption might raise up to 0.35A (tested with 'top d0').
The current consumed might have peaks as high as 0.50A @ 5V during start-up when different modules are initialized.
Make sure your supply is capable of providing at least half an ampere of current at 5V of voltage.
- A20-SOM + A20-SOM-EVB
The consumption of the combination A20-SOM + A20-SOM-EVB is betwen 0.10A and 0.15A when the A20-SOM-EVB is connected to a 12V voltage source (provided at the board's PWR jack).
During heavy load of the processor the consumption might raise up to 0.20A @ 12V (tested with 'top d0').
The current consumed might have peaks as high as 0.25A @ 12V during start-up when different modules are initialized.
CAD files
A20-SOM is considered commercial, proprietary design. The board file is not available to the customer. A pdf extracted from the original schematic is available at GitHub: A20-SOM schematics
KiCAD files of the connectors of A20-SOM/A20-SOM-EVB that are perfect as a template for own design can be found here: KiCAD templates A20-SOM
A20-SOM-EVB is considered Open Source Hardware, Eagle CAD files are available here A20-SOM-EVB sources
The CAD product used to design OLinuXino is Eagle and you can download evaluation free version from their web site. The evaluation version allows you to inspect the schematic and the board file sources.
How To?
Is it possible to boot Debian from NAND? Do you provide such image?
Yes, it is possible. Use the latest Debian Jessie image and write "nandinstall". More information can be found in this wiki article: installing Debian Jessie to the 4GB NAND memory
There are other people who are also successful in booting Debian from the NAND. Make sure to check on the forum. Make sure to check the number of very good and optimized A20-OLinuXino Debian images by Igor Pečovnik. There are also his instructions for NAND installation of Debian: link to his web-site
How to correctly power off OLinuXino running from NAND Flash
In this Blog post we explain what are the problems. This is common problem for all computers running OS. Here you can read more about MLC NAND Flash and Linux file system.
How to build the official Debian Linux image for A20-SOM?
Build instructions and required files for the latest Debian Jessie images: build instructions and required files at the GitHub page
Build instructions and required files for the latest Debian Wheezy images: instructions and files at the GitHub page
How to download new Android image to the NAND memory of my A20-SOM-4GB board?
In order to download the Android image to the NAND memory of the board follow these steps:
1. Install and run PhoenixSuit (can be found here: google drive location).
2. Download and extract the latest official image - can be found above in the Android section of this article. Make sure that the download link you visit clearly indicates that the image is suitable for the NAND memory since there are images suitable for microSD card also. The images suitable for the microSD memory and those suitable for microSD card are different. However, the upload method is almost identical – using PhoenixSuit.
3. Go to firmware tab of the program and point to the already downloaded and extracted Android image.
4. Disconnect the power supply and USB cable from the A20 board.
5. Press and hold RECOVERY button, apply power supply (the requirement various depending on whether you use the board stand-alone or on top of A20-SOM-EVB), release RECOVERY button.
6. Connect USB cable to the mini USB connector.
7. You will be asked for drivers for the bootloader. Navigate to the folder where you extracted the PhoenixSuit and install the drivers from the respective executable (or manually point the installer to the drivers folder in the PhoenixSuit installation path).
8. PhoenixSuit will detect the board and would ask whether you wish to also of writing the image. Choose method of writing the image and confirm your wish to write the image.
9. Wait till upgrade succeeds
Note that it is not recommended to have your mini USB connected to an external USB hub. This might cause delays and might distort the signal levels. Always test with the USB connected straight to the USB ports of your computer.
How do I write the official Android image to a micro SD card for my A20 board?
A: First download one of the official Android images, which might be found in the Android section above.
Make sure that the download link you visit clearly indicates that the image is suitable for the microSD card since there are images suitable for NAND memory also. The images suitable for the microSD memory and those suitable for NAND card are different. However, the upload method is almost identical – using PhoenixSuit.
There are two types of Android images for microSD card that we usually provide and each of them has to be downloaded to a microSD card using a different method. The image provided for microSD card is either the native Android image that can be downloaded to the card via a software tool like PhoenixSuit (through the board) or an image taken from an already prepared microSD card that requires to simply write the image (through a microSD card reader).
It is more likely that you have an Android image that requires a simple copy to a card. If that is the case you can follow the exact steps as for Linux (e.g. using "Win32 Disk Imager" or "dd" command).
In order to prepare a microSD card with a native Android you will need a software tool called PhoenixSuit and then:
1. Install and run PhoenixSuit (can be found here: download from google drive)
2. Go to the firmware tab of the program and point to a valid Android image (note that the images on Google drive are compressed and you have to extract the archives to .img files to be able write them with PhoenixSuit)
3. Disconnect the power supply and USB cable from the A20 board. Put an SD card in micro SD holder. We recommend 4GB class 10 card.
4. Press and hold RECOVERY button, apply power supply (the requirement various depending on whether you use the board stand-alone or on top of A20-SOM-EVB), release RECOVERY button.
5. Connect USB cable to the mini USB connector.
6. You will be asked for drivers for the boot-loader. Navigate to the folder where you extracted the PhoenixSuit and install the drivers from the respective executables (or manually point the installer to the drivers folder in the PhoenixSuit installation path).
7. PhoenixSuit will detect the board and would ask for the method of writing the image. Choose method of writing the image and confirm your wish to write the image.
8. Wait till upgrade succeeds
Note that it is not recommended to have your mini USB connected to an external USB hub. This might cause delays and might distort the signal levels. Always test with the USB connected straight to the USB ports of your computer.
Important: When Android runs for very first time it takes several minutes to initialize all files and buffers please do not cut the power supply during this process! Also when fresh image is installed fast boot may be disabled, which means that when you apply power supply after few seconds Android will go in sleep mode and you have to press POWER button to start it, you can change to fast boot when you power off there is dialog box asking you if you want next boot to be fast boot, you have to check this box before you power off. Also note that you must do touch screen calibration when you run Android for very first time which might require a mouse.
How do I write the Linux image to a micro SD card to use with my A20 board?
To write a Linux image to an SD card under Windows we use Win32 Disk Imager):
- Download Win32 Disk Imager Win32 Disk Imager
- Insert card
- Start program
- Select file
- Click "write"
To write a Linux image to an SD card under Linux:
For instance you have an image with the file name of "debian_2g.img". It would be downloaded to the SD card connected to a Linux machine using one of the following commands:
- # dd bs=4M oflag=sync if=debian_2g.img of=/dev/sdX
or
- # cp debian_2g.img /dev/sdX
where X is the uSD card.
I don't have neither serial cable, nor HDMI monitor. I also can't access the local Ethernet network. Can I somehow access the board anyway?
The latest official Debian Linux image allows the use the USB_OTG connector for SSH connection without the need of a LAN cable or a serial cable. You can use a mini USB cable connected between your host PC and the on-board mini USB connector. For connection convenience there is a DHCP server running specifically for USB0 interface. The DHCP server should give IP address to the new USB0 interface of your host PC so you can make SSH connection from your PC to the default board IP address of the USB0 interface – 192.168.2.1.
You can connect to the board using a mini USB cable and an SSH client (if you use Windows you might use "puTTY", for example) at address 192.168.2.1.
For Windows operating system - upon connection, the board should show up in "Windows Device Manager" as "RNDIS Ethernet Gadget". You might be asked to install a driver. The drivers can be found online as "RNDIS driver" (Remote Network Driver Interface Specification). The drivers are provided by Microsoft and they should be available for every Windows distribution - refer to the respective files and articles provided by Microsoft on how to install the required drivers.
How to change HDMI, VGA and LCD resolutions in the official Debian image?
The default SD card setup is made with settings for HDMI 720p/60Hz. If you want to change to some other LCD, VGA or HDMI resolution then you have to start change_display.sh script file in /root directory. When you are logged as super user in the board type:
For Debian Wheezy releases: ./change_display* (* = press 'tab' to auto-complete) For Debian Jessie releases: change_display* (* = press 'tab' to auto-complete)
and press "Enter".
Note that the script should be executed as super user. Under the command line interface you are automatically logged as super user (user "root", password "olimex"). However, under the graphical environment you are not auto-logged as super user and you must type "sudo" before the command (in the GUI the super-user is "olimex" and the password is "olimex")
Then choose the resolution and the interface(LCD, HDMI or VGA). Note that the selection of a specific resolution is done by navigating with the arrow keys and pressing "space" button. Make sure the asterisk marks your selection properly.
The supported resolutions are:
For LCD:
- 1. 4.3" (480x272)
- 2. 7" (800x480)
- 3. 10" (1024x600)
- 4. 15.6" (1366x768)
Important: initially the boards are calibrated for a specific display. If you re-write the image (no matter whether the SD card or the NAND memory) you would need to use a mouse to calibrate the display initially. It might be impossible to calibrate it via touching the display.
For HDMI:
- 0. 480i
- 1. 576i
- 2. 480p
- 3. 576p
- 4. 720p50
- 5. 720p60
- 6. 1080i50
- 7. 1080i60
- 8. 1080p24
- 9. 1080p50
- 10. 1080p60
- 11. pal
- 14. ntsc
For VGA:
- 0. 1680x1050
- 1. 1440x900
- 2. 1360x768
- 3. 1280x1024
- 4. 1024x768
- 5. 800x600
- 6. 640x480
- 7. 1920x1080
- 8. 1280x720
How to edit board configurations and definitions in the official Debian Linux?
Do you want a custom video resolution output? Do you need a different port definition? Do you need to change the hardware defitions of the board?
You would need to edit the board's script.bin/script.fex file. How to do it is described in a separate article: How_to_edit_board_configurations_and_definitions_in_the_official_Debian_Linux.
How to generate Arch Linux image?
Recent forum post by user progmetalbg here: at Olimex forums
Older step by step instructions on how to build Arch Linux image for another A20 board
How to detect and enable the Ethernet controller (if it is disabled by default)?
Note: in the previous Debian releases the Ethernet was auto-detected and initialized during boot BUT this was causing big delays in the start-up of the board if you didn't want to use Ethernet or if there wasn't Ethernet cable connected.
You can enable it by following these two steps:
1. To check under what name the LAN is associated write "ifconfig –a"
2. If, for example, it is under eth0 name, then write: "dhclient eth0"
This should enable the Ethernet and then SSH would also be available.
How to install Android on SD-card?
How to access UART, I2C, GPIOs under Android?
Use our Open Source OLinuXino A20-TOOLS
How to control PWM under Linux?
There is an article here: how to add pwm
How to build the Android 4.2.2 image for A20-OLinuXino-MICRO?
First you need to Download the A20 SDK2.0 Linux Kernel 3.4
Second you need to configure your environment read the instructions here
Then Build the kernel, kernel modules and u-boot
cd lichee ./build.sh -psun7i_android
When done, continue with Bulding the android image:
cd ../android4.2 cd device/softwinner/ tar zxfv olinuxino-a20.tgz cd ../../ source build/envsetup.sh lunch #select olinuxino-a20_eng extract-bsp make -j4
Dave from Axon instruments wrote more detailed blog post about how he generates the Android image]